In this article, let us learn what causes ModuleNotFoundError and see how we can fix that and get our code up and running again!
Troubleshooting any errors will include the following steps
Let us start by understanding the ModuleNotFoundError and its causes!
Step#1: Understanding ModuleNotFoundError and its Causes
What Is ModuleNotFoundError?
A short one line explanation would be
ModuleNotFoundError is an exception that is raised when Python fails to locate and import a module.
embeddedinventor.com
But then this much is obvious from the name of the Exception!
Let us see when/why/how Python will fail while importing modules and how to actually fix that!
If you are in the first steps of your Python journey and you are not 100% clear about what exceptions are, I strongly recommend reading our article on Exceptions before proceeding with this one!
Exceptions in Python: Explained for Beginners!
There we have explained the concept of exceptions from a beginner perspective with the goal that you will leave away with an intuitive feeling on what exceptions actually are and what their place is in the world of programming!
What Causes ModuleNotFoundError?
Here’s how that would look in action:
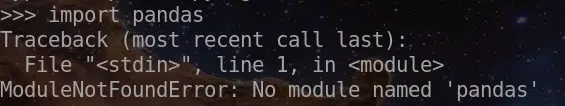
>>> import pandas as pd
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pandas'
In the above example, I tried to import the module ‘pandas’.
Normally while executing any import statement, Python simply finds where the module is and load it into the workspace.
In this case python failed to locate the pandas library and hence it raised the ModuleNotFoundError.
But then why did it fail?
There are several causes that might lead to failure in locating the module we wished to import, some of them are
- Module is not installed in your computer
- You have entered the name of the module incorrectly
- Python’s environment is setup incorrectly
Now that we have learnt all the causes that can lead to ModuleNotFoundError, we are almost there to get our code up and running again, lets move on to Step#2!
Step#2: Figuring Out the Exact Cause in your situation
The next step is to obviously figure out which of the 3 scenarios caused your issue!
Before getting into that here is a pro tip for you, to fix not just ModuleNotFoundError but any error in Python. Whenever your program crashes with an Exception, (take a deep breath and) have a look at the huge wall of error text that just got printed on your screen!
There is actually a lot of information contained in the error message, if you wish to learn the tricks then set aside 10mins of your time and read the following article!
Python: Details contained in an Exception
For visual learners out there we have also made an interesting video on that topic!
Coming back to the topic let us take a closer look at each of these causes so that you can figure out which one of these caused the problem for your particular case!
Cause#1: Module Not Installed
This is by far the most common cause of ModuleNotFoundError, so lets tackle it first!
If you are following a tutorial and you are trying out their code and ran into ModuleNotFoundError, then there is a good chance that the problem is you have not installed the necessary packages in your system!
In Python it is important to understand that
Not all the modules that are available comes as part of the standard installation package
embeddedinventor.com
If it were so, then the size of the python installer will probably hundreds of GBs!
Hence only a few selected ones that are most commonly used are packed into the standard installer, and if we need something that is not available in the standard installer, then we need to install is before importing it in our code!
For example in the screenshot below, I tried to import the pandas library before installing it in the first place!
Verify if module is present
You can check if a module is installed in your device or not by running the command shown below on your command prompt line interface. (command prompt or Powershell if you are on windows, and the the terminal app if you are on Mac or Linux)
pip show <module-name>Be sure you replace <module-name> with the right one! For example in my case I would type in
pip show pandasand I got the following result

If you are a beginner to the world of programming, and you don’t feel comfortable with the command line interface, then I suggest watching this video we made on that topic!
Fix for Cause#1: Install the module!
In python, installing a module is pretty easy and straight forward, all you need to do is enter the following command!
pip install <module-name>So in my case I would enter the command
pip install pandasAnd that would fetch the package and install in on my PC.
A successful installation will end something like
Successfully installed numpy-1.24.3 pandas-2.0.2 python-dateutil-2.8.2 tzdata-2023.3Once successfully installed, your code should run fine without ModuleNotFoundErrors!

But after you gave the pip install command if you are facing something like
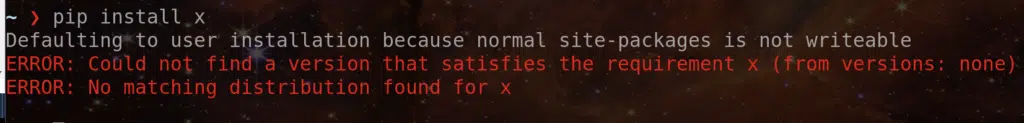
or if you are getting some other error while running your code, then read on!
Cause#2: Module Name is Incorrect
The python modules are usually acronyms or code names or shortened version of their full names, so there is a chance that you did not enter the name correctly.
For example if I write import panda instead of import pandas (note the missing s in the end) you would still run into ModuleNotFoundError as shown below
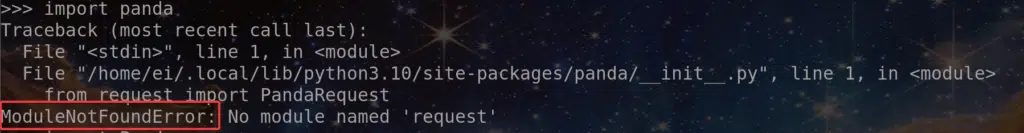
This can also happen if you don’t have some “captialization issue” as everything is case-sensitive in the programming world!
For example in the code below, I have the spelling correct, but I used “P” instead of “p”
import PandasThis will also result in ModuleNotFoundError as shown below
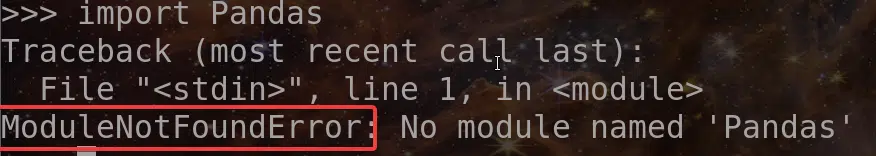
Fix for Cause#2: Double-check the module name!
The fix for this case is simple! Just make sure you have spelt the module name correctly and used the correct case in your spelling!
You can always google the line “import <module-name>” to figure out the correct way to write the module name!
Cause#3: Incorrect Python Environment Usage
This one is for advanced programmers out there who use virtual environments for development!
If you have multiple environments set up in your system, you may be using the wrong environment in which the module may not exist.
Fix for Cause#3: Double-check to make sure you are in the correct environment!
Check if you are using the correct environment and then verify if the environment you are using has the module installed!
I hope by now you got the code up and running again!
If so we have reached the end of the road! Don’t forget to celebrate!

For the next step in your Python journey I invite you to master some of the most common errors you will run into in your daily life as a Python developer. We have compiled a list of just 7 exceptions that you need to focus on if you wish to gain mastery of Exceptions in Python!
7 Most Common In-Built Exceptions in Python!
If you are a visual learner here is a YouTube video that we made on that same topic!
And with that, I end this article.
I hope you enjoyed reading this article and found it useful!
Feel free to share it with your friends and colleagues!
If your thirst for knowledge has not been quenched yet, here are some related articles that might spark your interest!
Related Articles
7 Most Common In-Built Exceptions in Python!
Python Exceptions: Explained for Beginners!
Python: When To Use Custom Exceptions? Explained!
Python TypeError: A Step By Step Troubleshooting Guide!
Thanks to Namazi Jamal for his contributions in writing this article!